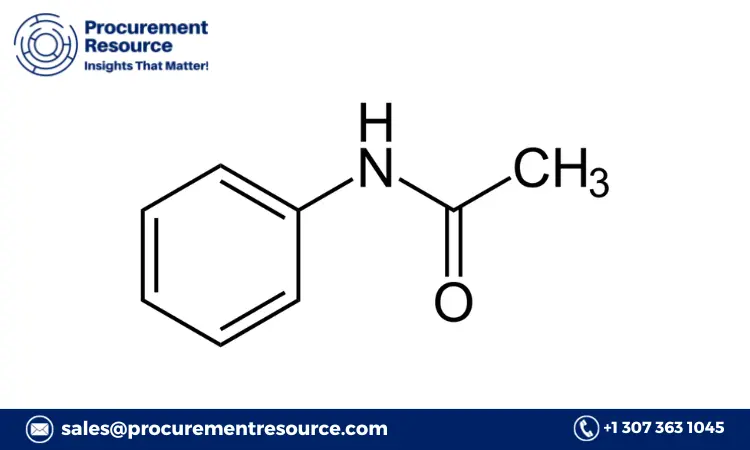
Linear Alkyl Benzene (LAB) is an essential intermediate in the production of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS), which is widely used in detergents and cleaning products. Understanding the production costs of Linear Alkyl Benzene is crucial for manufacturers, suppliers, and industry stakeholders to optimize operations and make informed financial decisions. This article provides a detailed analysis of the production costs associated with LAB, including raw material costs, production processes, and other contributing factors.
Production Process of Linear Alkyl Benzene
The production of LAB primarily involves two key processes: alkylation and hydrogenation. Here’s a simplified overview of these processes:
- Alkylation:
- Raw Materials: The primary raw materials for LAB production are benzene and long-chain linear olefins (C10-C14). Olefins are usually derived from the refining of kerosene or from ethylene through the oligomerization process.
- Process: Benzene is alkylated with linear olefins in the presence of a catalyst (typically HF or AlCl3) to produce a mixture of mono- and dialkylbenzenes. The monoalkylbenzene is the desired product, while dialkylbenzenes are considered impurities and must be minimized.
- Hydrogenation:
- Process: The alkylation mixture undergoes hydrogenation to remove any unsaturated compounds and to improve the stability of the LAB. This step is crucial for producing high-quality LAB suitable for detergent manufacturing.
Request For Free Sample: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/linear-alkyl-benzene/request-sample
Factors Influencing LAB Production Costs
Several factors contribute to the overall cost of producing LAB:
- Raw Material Costs:
- Benzene: The price of benzene is influenced by crude oil prices and the supply-demand dynamics of the petrochemical industry.
- Olefins: The cost of linear olefins varies depending on the source (kerosene or ethylene) and the efficiency of the oligomerization process.
- Catalyst and Chemical Costs:
- The type and quantity of catalysts (e.g., HF or AlCl3) used in the alkylation process significantly impact production costs. Catalyst regeneration and disposal also add to the costs.
- Energy Costs:
- Energy consumption in the form of electricity and fuel is a major component of production costs. The hydrogenation process, in particular, requires significant energy input.
- Labor and Maintenance:
- Labor costs for operating and maintaining production facilities are another key factor. Regular maintenance to ensure efficient operation and to avoid downtime is crucial.
- Environmental and Regulatory Compliance:
- Adherence to environmental regulations, especially concerning the handling and disposal of hazardous chemicals (e.g., HF), can add to the production costs. Investment in safety and environmental protection measures is necessary.
- Capital Costs:
- The initial investment in setting up a production plant, including equipment, infrastructure, and technology, is a significant part of the overall cost structure.
Regional Variations in Production Costs
The production costs of LAB can vary significantly across different regions due to variations in raw material availability, labor costs, energy prices, and regulatory environments. Here’s a brief regional analysis:
- North America:
- Advantages: Abundant raw material supply, advanced technology, and efficient production processes.
- Challenges: Higher labor and regulatory compliance costs.
- Europe:
- Advantages: Advanced technology and stringent quality standards.
- Challenges: High energy and labor costs, strict environmental regulations.
- Asia-Pacific:
- Advantages: Lower labor costs, increasing availability of raw materials, and expanding industrial base.
- Challenges: Variable energy costs and regulatory environments.
- Middle East:
- Advantages: Abundant and cheap raw materials (especially petrochemicals), lower energy costs.
- Challenges: Political and economic instability in certain areas.
Future Outlook and Cost Optimization
The outlook for LAB production costs will be influenced by several factors, including advancements in production technology, fluctuations in raw material prices, and changes in regulatory environments. Here are some strategies for optimizing production costs:
- Technology Upgrades: Investing in advanced production technologies to improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
- Raw Material Sourcing: Securing long-term contracts with suppliers to stabilize raw material costs.
- Process Optimization: Implementing process optimization techniques to maximize yield and minimize waste.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Adopting sustainable practices to reduce environmental compliance costs and improve overall operational efficiency.
Conclusion
The production cost of Linear Alkyl Benzene is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including raw material costs, production processes, energy consumption, and regulatory compliance. By understanding these factors and implementing cost optimization strategies, manufacturers can improve their competitiveness in the market. Staying abreast of technological advancements and regulatory changes will be crucial for the long-term success of LAB production.
Harry
